AL01 SAP Alert Monitor
AL02 Database alert monitor
AL03 Operating system alert monitor
AL04 Monitor call distribution
AL05 Monitor current workload
AL06 Performance: Upload/Download
AL07 EarlyWatch Report
AL08 Users Logged On
AL09 Data for database expertise
AL10 Download to Early Watch
AL11 Display SAP Directories
AL12 Display table buffer (Exp. session)
AL13 Display Shared Memory (Expert mode)
AL15 Customize SAPOSCOL destination
AL16 Local Alert Monitor for Operat.Syst.
AL17 Remote Alert Monitor for Operat. Syst.
AL18 Local File System Monitor
AL19 Remote File System Monitor
AL20 EarlyWatch Data Collector List
AL21 ABAP Program analysis
AL22 Dependent objects display
CREF Cross-reference
BD64
BSVW Linkage Status Update-Workflow Event
CMOD Enhancements
DB01 Analyze exclusive lock waits
DB02 Analyze tables and indexes
DB03 Parameter changes in database
DB11 Early Watch Profile Maintenance
DB12 Overview of Backup Logs
DB13 Database administration calendar
DB14 Show SAPDBA Action Logs
DB15 Data Archiving: Database Tables
DB16 DB System Check: Monitor
DB17 DB System Check: Configuration
DMIG Start Transaction for Data Migration
DB2 Select Database Activities
DB20 DB Cost-Based Optimizer: Tab. Stats
DB21 DB Cost-Based Optimizer: Config.
DB24 Database Operations Monitor
DB26 DB Profile:Monitor and Configuration
DB2J Manage JCL jobs for OS/390
DBCO Database Connection Maintenance
FILE Cross-Client File Names/Paths
NACE WFMC: Initial Customizing Screen
OAA1 SAP ArchiveLink: Maint.user st.syst
OAA3 SAP ArchiveLink protocols
OAA4 SAP ArchiveLink applic.maintenance
OAAD ArchiveLink Administration Documents
OAC2 SAP ArchiveLink: Globaldoc. types
OAC5 SAP ArchiveLink: Bar code entry
OACA SAP ArchiveLink workflow parameters
OAD0 SAP ArchiveLink: Objectlinks
OAD2 SAP ArchiveLink document classes
OAD3 SAP ArchiveLink: Link tables
OAD4 SAP ArchiveLink: Bar code types
OAD5 SAP ArchiveLink: Customizing Wizard
OADR SAP ArchiveLink: Print list search
OAM1 SAP ArchiveLink: Monitoring
OAOR SAP ArchiveLink: Storeddocuments
OARE SAP ArchiveLink:St.syst.return codes
OS01 LAN check with ping
OS03 O/S Parameter changes
OS04 Local System Configuration
OS05 Remote System Cconfiguration
OS06 Local Operating System Activity
OS07 Remote Operating SystemActivity
OSS1 Logon to Online ServiceSystem
OY18 Table history
OY08 Development Class Overview
PFCG Activity Group
PFUD Authorization Profile comparison
RLOG Data migration logging
RZ01 Job Scheduling Monitor
RZ02 Network Graphics for SAP Instances
RZ03 Presentation, Control SAP Instances
RZ04 Maintain SAP Instances
RZ06 Alerts Thresholds Maintenance
RZ08 SAP Alert Monitor
RZ10 Maintenance of profile parameters
RZ11 Profile parameter maintenance
RZ12 Maintain RFC Server Group Assignment
RZ20 CCMS Monitoring
RZ21 Customize CCMS Alert Monitor
SA38 ABAP/4 Reporting
SAD0 Address Management call
SADC Address: Maint. communication types
SALE Display ALE Customizing
SAINT Plug-in Installation
SARI Archive Information System
SAR3 Customizing Archiving
SAR4 Define Archiving Class
SAR5 Assign Archiving Class
SAR6 Archiving Time Generator
SARA Archive management
SARL Call of ArchiveLink Monitor
SARP Reporting (Tree Structure): Execute
SART Display Reporting Tree
SB01 Business Navigator - Component View
SB02 Business Navigator - Process flow vw
SBAS Assignments to Process Model Elemts
SC38 Start Report Immediately
SCAT Computer Aided Test Tool
SCC0 Client Copy
SCC1 Client Copy - Special Selections
SCC2 Client transport
SCC3 Client Copy Log
SCC4 Client administration
SCC5 Client Delete
SCC6 Client Import
SCC7 Client Import – Post Processing
SCC8 Client Export
SCC9 Remote Client Copy
SCCL Local Client Copy
SCDO Display Change DocumentObjects
SCMP View / Table Comparison
SCOM SAPcomm: Configuration
SCON SAPconnect - Administration
SCPF Generate enterprise IMG
SCPR1 Customizing Profiles : Maintenance Tool
SCPR2 Comparing Customizing profiles
SCUA Central User Administration : Distribution Model Assigment
SCUG Central User Administration Structure Display
SCUL
SCUM Central User Administration Field Selection
SCU0 Table Analyses And Comparison
SCU1 Table Comparison - Export to Tape
SCU2 Table Comparison Against Tape
SCU3 Table History
SD11 Data Modeler
SDBE Explain an SQL Statement
SECR Audit Information System
SE01 Transport and Correction System
SE02 Environment Analyzer
SE03 Transport Utilities
SE06 Set up Workbench Organizer
SE07 Transport System Status Display
SE09 Workbench Organizer (Initial Screen)
SE10 Customizing Organizer
SE11 Data Dictionary Maintenance
SE12 Data Dictionary Display
SE13 Maintain Technical Settings (Tables)
SE14 Convert Data Dictionary tables on Database Level
SE15 Repository Info System
SE16 Display Table Content
SE17 Generate Table Display
SE30 ABAP Objects Runtime Analysis
SE32 ABAP Text Element Maintenance
SE33 Context Builder
SE35 ABAP/4 Dialog Modules
SE36 Logical database
Thursday, July 31, 2008
Useful SAP System Administration Transactions
Changing the Title of SAP Transaction
Sometimes, internal user or customer might request you to change the Title of the SAP Transaction code to a more meaningful one and SAP allows this to be done painlessly.
The steps to change the Title of any SAP transaction code are as follows:
First, goto tcode SE63
On the top left Menu of the screen - Click Translation - Short texts - Transactions
For example, assuming you want to change the title of the tcode FB01 from Post Document to Post Document for G/L. On the first screen, fill in the following information:
Transaction code - FB01
Source Language - English
Target Languate - English
To change the Title, click the Edit button
On the second line, type in the Title (For e.g. Post Document for G/L) you want for the transaction code
Click the Save button
Now, called up the transaction code /nFB01 again and you should be able to view the new Title.
Please note that it works for most of the Transaction code except for those new Enjoy transaction code in 4.6x.
Search for SAP Basis Transaciton codes
You can access all the transaction codes by using the transaction code 'SDMO'.
This is the transaction code for the Dynamic Menu.
Based on your search string, you can get all related transaction codes for all the SAP application modules.
For e.g. the Search text for ADMIN returns the following results:
----------------------------------------------------------What the difference between tcode SE09 & SE10?
|Tcode|Transaktionstext |
----------------------------------------------------------
|ADOK |AM: System Administration Guide |
|BALE |Area Menu for Administration |
|BDMO |ALE CCMS Group Administration |
|CATSX|Time Sheet Admin.: Initial Screen |
|CICY |CTI Administration |
|CJV6 |Maintenance: Version administration |
|CN84 |PS: Archiving project - admin. |
|COA4 |PP: Archiving order - administration |
|CSADM|Content Server Administration |
|FC_BW|Administrator Workbench |
|FDTA |TemSe/REGUT Data Administration |
|FDTT |Treasury Data Medium Administration |
|FO86 |Change active admin.contract fees |
|FO8E |Create admin.contract event |
|FO8F |Change admin.contract event |
|FO8G |Display admin.contract event |
|FO8H |Admin.costs acct sttlmnt simulation |
|FOART|REsearch: Administration Web-User |
|HRCMP|Compensation Administration |
|HRCMP|Budget Administration: Display |
|HRCMP|Budget Administration: Change |
|IM_AR|Admin. of App. Request Archives |
|KA18 |Archive admin: assess., distr., ... |
|KE72 |Archive Administration: Line Items |
|KE73 |Archive Administration: Totals Recs |
|KPRO |KPRO Administration |
|OAAD |ArchiveLink Administration Documents |
|OG00 |Personnel Administration Customizing |
|OG01 |Personnel Administration Customizing |
|OMSM |CS MM Set Up Administrative Data |
|OOCM_|Compensation Administration Settings |
|OOML |Room Administration Mail Connection |
|OOPC |Administration: Personnel No. Check |
|OY22 |Create subadministrator Customizing |
|OYEA |IDoc administration |
|PA97 |Compensation administration - matrix |
|PA98 |Compensation Administration |
|PA99 |Compensation Admin. - Release Report |
|PACA |PF administration |
|PAT1 |Personnel Administration infosystem |
|PC00_|CBS survey salary administrations |
|PC00_|Tax Certificates - Administration 16 |
|PP26 |Plan Scenario Administration |
|PP2D |Administer Payroll Results |
|PSO5 |PD: Administration Tools |
|PUCA |PC administration for PF |
|PVSEA|Administer Search Engine |
|QD25 |Archiving Notifications: Admin. |
|S002 |Menu Administration |
|SA02 |Academic title (cent. addr. admin.) |
|SA04 |Name prefixes (centr. addr. admin.) |
|SA05 |Name suffix (centr. addr. admin.) |
|SA07 |Address groups (centr. addr. admin.) |
|SA08 |Person groups (centr. addr. admin.) |
|SA09 |Internat. versions address admin. |
|SA10 |Address admin. communication type |
|SARA |Archive Administration |
|SBPT |Administration Process Technology |
|SCC4 |Client Administration |
|SCON |SAPconnect - Administration |
|SCOT |SAPconnect - Administration |
|SCUA |Central User Administration |
|SCUM |Central User Administration |
|SE78 |SAPscript: Graphics administration |
|SECST|Administration of Secure Memory |
|SENG |Administration of External Indexes |
|SENGE|Explorer Index Administration |
|SIAC1|Web Object Administration |
|SLICE|Administer SAP Licenses |
|SLWA |Translation Environment Administratn |
|SM14 |Update Program Administration |
|SP12 |TemSe Administration |
|SPAD |Spool Administration |
|SPAT |Spool Administration (Test) |
|SPHA |Telephony administration |
|SPHB |SAPphone: System Administration |
|SSAA |System Administration Assistant |
|SSCA |Appointment Calendar: Administration |
|SSCA1|Appointment calendar: Administration |
|SSO2 |Workplace Single Sign-On Admin. |
|SSO2_|Workplace Administration SSO2 Ticket |
|STMA |Proposal Pool Administration |
|SURAD|Survey Administration |
|SURL_|Personalization for URL Gen. Admin. |
|SUUMD|Display User Administration |
|SWDC |Workflow Definition: Administration |
|SWEAD|Event Queue Administration |
|SWEQA|Event Queue Administration |
|SWEQA|Queue Administrator Maintenance |
|SWIA |Selection rep. for work items(admin) |
|SWRK |Administrtation using work areas |
|SWUF |Administration of Runtime System |
|SWUL |Customizing: Process Administrator |
|SWUX |SAPforms Administration |
|SYSAD|System Administration: Task List |
|S_ALR|IMG Activity: CIC_V_CCMCTIADMIN |
|S_ALR|IMG Activity: SIMG_EURO_ADMINUSER |
|S_BCE|IMG-Aktivität: BCDIGSI_ADMIN |
|S_PH0|InfoSet Query: Administration |
|S_PH0|InfoSet Query: Administration |
|S_PH0|InfoSet Query: Administration |
|S_PH0|InfoSet Query: Administration |
|S_PH0|InfoSet Query: Administration |
|TBD0 |Datafeed: Adminster Archives |
|TBD3 |Datafeed: Market data administration |
|TBD6 |Datafeed: Log file administration |
|WE46 |IDoc administration |
|WORKI|Administrtation using work areas |
----------------------------------------------------------
SE09 transaction is for workbench transport request wherein the developers can track their changes or modifications to the workbench objects .
Whereas SE10 is a customising transport request transaction.this is used for displaying customising requests. Sometimes this may be restricted to business analysts.
How to list all transactions executable for a role.
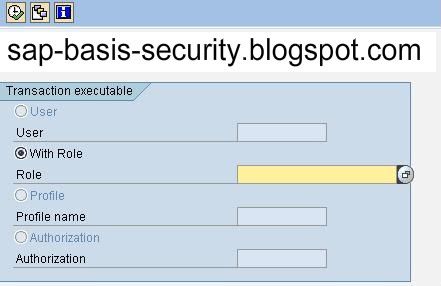
and enter the role name and press F8 to get the results.
but this gives only tcode in the menu of the role.
It will not show the tcodes that are added manually to the role in S_TCODE object.
To find all tcode executable for role along with the tcode that are present in the tcd field..
goto se16 enter agr_1251 and click on data browser button

enter the role name in agr_name field and enter tcd in FIELD field ash shown in figure.

Then click on execute button
 or press F8 to execute and you will see the list of tcodes executable for that role as below
or press F8 to execute and you will see the list of tcodes executable for that role as below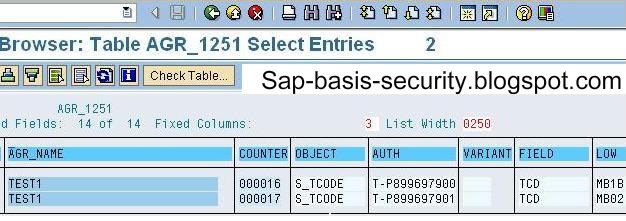
List of Tcodes executable for a User in SAP
Use SUIM .
goto SUIM tcode then drill down
transactions -----> executable for user.
Then run that program and enter the USERID of the user and press F8. Then you will see the list of tcodes executable for the user
How to view recently accessed transactions by users in SAP
1) Turn the audit log on by using SM19 and SM20 and analyze the audit logs.Put filters while setting up these logs so that you can see the specific data.
2) In ST03N / ST03, you can analyze the transactions run by users by selecting the "User Profile" under the "Analysis Views" section.
Note: ST03N keeps limited data
How to find sap transaction codes IN SAP
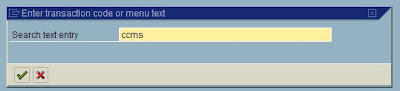 You will see the out put as
You will see the out put as
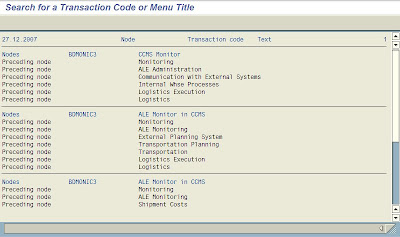
Sap Basis Transaction Codes 343
ABAP & Tables Related Transactions
SA38 To execute a Abap program
SE38 ABAP Editor
SE11 ABAP/4 Dictionary Maintenance
SE80 ABAP Development Work Bench
SE16N General Table view ( very Useful)
SE16 Data Browser or table viewer
Administration
AL11 Display SAP Directories
BD54 Maintain Logical System
OSS1 Logon to Online Service System
SALE IMG Application Link Enabling(ALE)
SARA System Archive Administration
SCU0 Customizing Cross-System Viewer
SICK Installation Check (System Initial Consistency Check)
SM01 Lock/unlock Transactions
SM02 Send System Messages to all users
SM04 List of Users logged into the Client
SM12 Display and Delete Locks
SM13 Display Update Request Records
SM14 Update Program Administration
SM21 System Log
SM35 Batch Input Overview
SM50 Work Process Overview
SM51 SAP Servers list
SM56 Number Range Buffer
SM58 Transactional RFC overview
SM59 Display and Maintain RFC Destinations
SM66 Global Work Process Overview
SAINT SAP Add-on Installation Tool
SPAM SAP Support Package Manager (SPAM)
SPAU Display modified DE objects
SPDD Display modified DDIC objects
ST11 Display Developer Traces
ST22 ABAP/4 Runtime Errors
SU56 User Buffers
SMT1 Maintain or display Trusted systems
Client Administration commands
SCC3 Client Copy Analysis Log
SCC4 Client Administration
SCC5 Client Delete
SCC7 Client Import Post-Processing
SCC8 Client Export
SCC9 Remote client copy
SCCL Local Client Copy
SCC1 Client Copy by transport request
Configuration
FILE Cross-Client File Names/Paths
RZ04 Maintain Operation Modes and Instances
RZ10 Maintenance of Profile Parameters
RZ11 Profile parameter maintenance
SE93 Maintain Transaction Codes
SWU3 Automatic Workflow Customizing
SPRO Customizing: Execute project
SM63 Display/Maintain Operating Mode Set
Database Administration
DB01 Analyze exclusive lockwaits (database snapshot)
DB02 Analyze tables and indexes (Space History overview)
DB03 Configuration Parameter Changes
DB12 DB Backup and Recovery Monitor
DB13 DBA Planning Calendar
DB15 Tables and archiving objects
Jobs
SM36 Define or schedule a Background Job
SM37 Background Job Overview & Maintenance
SM49 Execute External Operating System commands
SM62 Display or maintain Events
SM64 Trigger Event in backgroung processing
SM65 Background Processing Analysis Tool (testing)
SM69 Display or Maintain External OS Commands
Monitoring
AL04 Sap Performance Monitor
AL16 Operating System Monitor
RZ20 CCMS Monitoring
AL08 Current Active Users
OS01 LAN check by ping
RZ01 Job Scheduling Monitor (external program)
RZ03 Presentation, Control SAP Instances
ST01 System Trace
ST02 Setups/Tune Buffers
ST03 Performance, SAP Statistics and Workload analysis
ST03n Work load Analysis
ST04 Performance: Database snapshot
ST05 Performance Analysis
ST06 Operating System Monitor
ST07 Application monitor : User distribution
ST10 Table call statistics
STAT Local transaction statistics
Spool
SP01 Output Controller
SP02 List of the users spool requests
SP11 TemSe directory
SP12 TemSe Administration
SPAD Spool Administration (defining printers etc…)
Transports
SE01 Transport Organizer
SE06 Set Up Workbench Organizer (Post-installation actions for transport organizer)
SE07 CTS Status Display (import monitor)
SE09 Workbench request Organizer
SE10 Customizing request Organizer
STMS Transport Management System
SM30 Table View Maintenance
SM31 Table Maintenance
User Administration
PFCG Profile Generator (Activity Group Maintenance)
SU01 User Maintenance (single user maintenance)
SU01D User Display (safe)
SU02 Maintain Authorization Profiles (depreciated)
SU03 Maintain Authorizations
SU05 Maintain Internet users
SU10 User Mass Maintenance (You cannot change user master data using this)
PFUD User Master Data Reconciliation
SMLG Maintain Logon Group
SUPC Mass generation of Profiles for activity groups
SUIM User Information system (very good transaction code)
One can find any information about a user using this t-code
Central User Administration
SCUA Activate/maintain CUA
SCUG Transfer user
SCUL Central User Management Log Transaction used to view CUA audit and error logs.
Related to Idocs
WEDI IDoc and EDI Basis
WE02 IDoc list display
WE07 IDoc statistics
WE46 IDoc administration
Other Transactions
HIER Internal Application Component Hierarchy Maintenance
WE20 Maintain Partner profiles
WE21 Port definition
WE47 Status Maintenance
Changing the Title of SAP Transaction
Sometimes, internal user or customer might request you to change the Title of the SAP Transaction code to a more meaningful one.
The steps are as follows:
Goto tcode SE63 . On the top left Menu of the screen - Click Translation ---> Short texts - --> Transactions
For example, assuming you want to change the title of the t-code su10 from user maintenance: Mass changes Initial Screen to Mass User changes . On the first screen, fill in the following information:
Transaction code - SU10
Source Language - English
Target Language - English
To change the Title, click the Edit button. On the second line (the one in dark yellow), type in the Title (For e.g. Mass User changes) you want for the transaction code. Click the Save button

Now, call up the transaction code /nSU10 again and you should be able to view the new Title.
Basis Tables Reorganization of Single Object
You have ARCHIVED the BSIS table (because of old data etc) and now this BSIS table has "holes" in physical structure and it's quite a large table.
Here are the steps to reorg. a single object:
1. Take a backup of your Oracle database.
2. Shutdown SAP
3. Start Oracle Database with Rollback Segment PSAPROLLBIG (all other smaller segments not started). Remember, the size of PSAPROLLBIG should be equal or larger than your BSIS table.
4. Ensure sapreorg directory has enough space for taking BSIS Oracle Export dump. The Oracle Export utility compresses the file to some extent.
5. Fire your SAPDBA from Unix level.
6. Go into SAPDBA "reorganisation" menu.
7. Select "Reorganize Single Table / Index"
8. Give BSIS as table name.
9. Start.
10. Don't Forget, first upgrade your SAPDBA tools first from OSS/SAPNet.
These include: 1. sapdba 2. brtools 3. brarchive 4. brbackup 5. brrestore 6. brconnect.
How to Increase the Tablespace free space?
Your tablespace PSAPBTABD is 92% used. How to increase the free space?
SAPDBA V3.1I - SAP Database Administration
____________________________________________________________________________
ORACLE version : 7.3.4.3.0
ORACLE_SID : ALD
ORACLE_HOME : /oracle/ALD
DATABASE : open
SAPR3 : 31H, 23 times connected
a - Startup/Shutdown instance h - Backup database
b - Instance information i - Backup archive logs
c - Tablespace administration j - Check (and repair) database
d - Reorganization k - Restore/Recovery
e - Export/import l - Show/Cleanup
f - Archive mode m - User and Security
g - Additional functions n - Help
q - Quit
Please select ==> c
____________________________________________________________________________
Tablespace administration
____________________________________________________________________________
Current value
a - Tablespace:
b - Log checks: no
c - Free space and fragmentation of all tablespaces
d - Check free space of objects in all tablespaces
e - Check free space of objects in tablespace
f - Alter tablespace Add Datafile
g - Create/drop tablespace
h - Display all tablespaces and datafiles
i - Display raw device drivers in /dev
q - Return
Please select ==> a
Enter tablespace name [%] ==> psapbtabd
____________________________________________________________________________
Tablespace administration
____________________________________________________________________________
Current value
a - Tablespace: PSAPBTABD
b - Log checks: no
c - Free space and fragmentation of all tablespaces
d - Check free space of objects in all tablespaces
e - Check free space of objects in tablespace PSAPBTABD
f - Alter tablespace PSAPBTABD Add Datafile
g - Drop tablespace PSAPBTABD
h - Display all tablespaces and datafiles
i - Display raw device drivers in /dev
q - Return
Please select ==> f
____________________________________________________________________________
Alter tablespace PSAPBTABD add datafile
____________________________________________________________________________
Current value
a - File system or raw device: file system
b - File size: 2088960 K (larger than free space)
c - Select path: /oracle/ALD/sapdata5
d - Alter suggested path: /oracle/ALD/sapdata5
free space: 3608 K
e - Display current files: 10 files, total (in DB): 77
s - Start (Add datafile)
q - Return
Please select ==> s
How to activate the IMG Change Log?
SCU3 transaction is used to see the IMG change logs for modified objects.
If your table change log is not active, it will gives you a message that :-
...table logging is switched off...
This particular setting can be changed in the following path :-
IMG--> Basis Components --> System Administration --> Tables changes recording
You can log changes made to the following tables:
- Control tables (system logic control)
- Customizing tables
What is recorded is always in the form of complete "before" images, that is, all entries as they appear before the changes.
The recorded data is compressed without buffering, and this is not an appropriate method for recording and managing large amounts of data. Activating logging impacts on performance as it entails twice as many database updates as would otherwise be the case, and the database storage load is also increased substantially.
It is recommend that you use logging for your production clients and Customizing clients so that you can see exactly where Customizing tables have been changed. Other than the reasons above, it is not recommended that you use this tool for application tables.
Two conditions have to be met for a table to be logged:
1. The table has to be selected for logging in the Dictionary (see Dictionary -> Table maintenance -> Technical configuration).
2. Logging also has to be set in the system profile
Set the rec/client (note the use of lowercase characters) profile parameter to one of the following values :-
- OFF: no logging at all (effectively a central system switch)
- nnn: logs client-specific tables in client nnn only
- mmm,nnn,ppp,...: logs client-specific tables in the named clients
- ALL: logs all client-specific tables in all clients.
Caution: Only in exceptional circumstances is it appropriate to use the 'ALL' setting. If, for example, the profile parameter is set to 'ALL' when you upgrade all test clients (including 000, the SAP client), these changes are recorded in the system log file. This reduces performance and requires a lot of database space.
The default setting is OFF (no changes are logged).
If logging is set in the ABAP Dictionary, changes to client-indepedent tables are always logged unless rec/client is set to 'OFF'
Use the ABAP programs RSTBHIST or RSVTPROT to analyze table changes. RSVTPROT allows you to analyze change logs both at table level and with reference to Customizing objects. To access the program, select an executable Customizing activity in IMG and choose Goto -> Change log.
Basis - Edit, create, delete or adjust your database table
Edit, create, delete or adjust your database table
The database utility is the interface between the ABAP Dictionary and the relational database underlying the R/3 System.
This tools allows you to delete all the data in the tables.
You can call the database utility from the initial screen of the ABAP Dictionary with
Utilities -> Database utility (Transaction SE14).
You can use the database utility to edit all the database objects that are generated from objects of the ABAP Dictionary.
These are database tables that are generated from transparent tables or physical table pools or table clusters, indexes, database views and matchcode pooled tables or matchcode views.
If you want to use the database utility, you need authorization for authorization object
S_DDIC_OBJ, e. g. S_DDIC_ALL.Finding any of the SAP tables that have been changed
During the production run of the SAP system, additional fields might have been added and you might have lost tracks of the SAP tables changes.
Transaction code SPDD have been created to help you to find all the SAP tables that have been modified.
Other ABAP Dictionary objects such as lock objects, matchcodes, and views, for which modification would not result in data loss, are not processed during the upgrade with transaction SPDD, but only after the upgrade is complete with transaction SPAU.
Transport Tables between Clients
Use report RSCLCCOP to transport user master records, profiles and authorizatons between clients in an R/3 system.
Start RSCLCCOP from the target client which the users and authorizations should be copied.
Do not use this report if the target client contains some users and authorizations you want to preserve.Copying table entries from client 000
I need to copy table entries from client 000.
I have identified which entries I need to copy through running RPULCP00 but I don't know how to move the entries.
The simplest way is to go into the table through SM31
Then in your top row of buttons there should be one called 'utilities' from here select 'adjust',
Then select the client that you want to compare/copy from (you need to have an RFC destination set up).
This will then show you the contents of the table in both clients and identify the status of each record, they will fall into the following categories:
ML Differences, logon client entry
MR Differences, comparison client entry
L Entry only exists in logon client
R Entry only exists in comparison client
Identical entries
(M) Differences only in hidden fields
You should be able to scroll down the table, select the entries that you want to import, then hit the 'adjust' button, then hit the 'copy all' button, then back out with the green arrow, and save your table.
That should do the job.
SAP Transaction Table
TSTC - SAP Transaction Codes
Used SE12 to display the tables.SAP Tablespace sizes in large databases
Robert and others following the thread,
First a little background on extents in our production system. We created the instance about 4 months prior to going live. As man of you know, getting down time during the last few months is nearly impossible, so we saw and let extents grow. In fact, by the time we went live, we had 2 objects over 450, 5 objects over 300, about 50 objects (tables and indices) that were over 100 extents, and we had hundreds of objects over 10 extents.
I agree to doing both planning for growth and monitoring growth. And the earlier in your SAP implementation you do this the better - which is something we did not do until after we created our productive instance.
We were very concerned about this situation and spoke to 3 or 4 different SAP consultants. We got the same answer from each - objects in high extents will have little or no performance impact. Like Sanjay mentioned, the consultants had no specific reason for this.
I do not believe you will find an SAP employed person who will say you should keep extents below a specific value. Also, I cannot definitively give that advice either.
Over the months we have all our objects below 100 extents. We have not seen a significant change in database response time. Our goal is to have all objects below 20 extents - which is a corporate standard.
But we will not ask for extra down time to reach this goal.
Good luck trying to keep objects below 10 extents. While data is "pumped" into the system during the weeks before going live, whatch the extents, they will take off. This also occurs after performing a SAP version upgrade.
Mark A. Kochanski
-----Reply Message-----
Subject: Re: BASIS: Tablespace sizes in large databases -Reply [3]
From: "Robert A. Simard"
Gentleman,
Why not do both? Planning for growth is critical. Monitoring daily can be automated via CCMS can it not? With proper alert thresholds, a system freeze can be thwarted long before extents reach 300 (max extents in my version of Oracle).
My question to you both is, how many extents are to many? I have heard from consultants that SAP says that, for performance reasons 10 is the limit. I do not understand the logic in this. Unless There is alot of fragmentation throughout the tables, why not 50 or 100? I just completed a Client Copy and have 4 tables in the BTABD tablespace that are over 17
extents. Is this to many? and should I lose the uptime for a reorg for 17 versus 10 extents?
I guess what I am asking is, since both of you seem to have put some thought into this, is there a hard-and fast number when in comes to an acceptable amount of extents? SAP seems to be overly conservative most of the time - was wondering if anyone has good numbers?
Thanks and have a great day.
~Bob
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Robert A Simard SAP-Basis Support, NT Sys. Admin.
"Whoever is first in the field and awaits the coming of the enemy, will
be fresh for the fight; whoever is second in the field and has to hasten
to battle will arrive exhausted."
Sun Tzu - The Art of War
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----Reply Message-----
Subject: Re: BASIS: Tablespace sizes in large databases -Reply [3] -Reply
From: Sanjay Shastri
Good suggestion and well received ;-)
Now to try and answer your question, looking at just Oracle ( or any DB ), you would think that too many extents would cause problems with your performance ( and that is quite true in most cases ). However, I believe I read on this list that SAP ignores the extent growth ( no explanation provided ) and that it 'really does not matter how large the number gets'.....
We have several tables that are over 150 extents and don't see too much of a performance glitch ( on an overall level ) but in practice, I do not let any table go beyond 100 extents in an SAP environment. Letting indices grow too much seems to have a much greater impact.
Any comments / insights?
- Sanjay
-----Reply Message-----
Subject: BASIS: Tablespace sizes in large databases -Reply -Reply
From: Sanjay Shastri
Mark,
would you be willing to risk a system freeze, even if it happens once? I happen to believe in the saying 'prevention is better than cure' !
You are correct that keeping up with extent growth and increasing the size of the next extent via SAPDBA controls the extent problem but, resizing the tables offers one advantage in that you plan better for growth and you are not bogged down by too much of an maintenance effort. System availability IS critical and minimizing downtime doesn't hurt... ;-)
- Sanjay
-----Reply Message-----
Subject: BASIS: Tablespace sizes in large databases -Reply -Reply
From: Mark Kochanski
Sanjay,
Tablespaces will grow and you can add space as needed but if you run out of extents on tables....tough luck!
Why Tough luck? Sure, if a table or index reaches max extents your system will freeze or go down, or certain transactions will have errors. .....
-----End of Reply Message-----SAP SQL Tuning Aid with Oracle RDBMS Statistics
*| Author Jayanta Narayan Choudhuri |
*| Flat 302 |
*| 395 Jodhpur Park |
*| Calcutta 700 068 |
*| Email sss@cal.vsnl.net.in |
*+---------------------------------------+
* SQL Tuning Aid in SAP
* ---------------------
* To tune SQLs effectively one must know relative row counts of tables
in the program.
* Also primary Keys & all indexes of all the selected tables are shown
all in 1 place.
* Then the ABAP programmer has to change navigation and logic to suit
indexes.
* The large tables are likely to be the "hot spots".
* As a last resort it may be necessary to add a new Index to SAP or Z
tables.
* Try with BSEG MSEG A004 RFBLG KAPOL MSEG VBFA
* The Code is given below for SAP with Oracle RDBMS. Should be easy to
adapt to SQLServer Informix DB2,
* if you know a bit of the DBA side of things.
REPORT ZSQLTUNE.
TYPE-POOLS: slis. "ALV Global types
***Table Declaration
TABLES: dd02l.
***Internal Tables Declaration
TYPES: BEGIN OF t_statsora,
num_rows TYPE i,
avg_row_len TYPE i,
last_analyzed TYPE ekbe-budat,
END OF t_statsora.
TYPES: BEGIN OF t_stats,
tabname TYPE dd02t-tabname,
tabclass TYPE dd02v-tabclass,
num_rows TYPE i,
avg_row_len TYPE i,
last_analyzed TYPE ekbe-budat,
ddtext TYPE dd02t-ddtext,
index0(80) TYPE c, "DD03L
index1(80) TYPE c, "1-6 from DD17S
index2(80) TYPE c,
index3(80) TYPE c,
index4(80) TYPE c,
index5(80) TYPE c,
index6(80) TYPE c,
END OF t_stats.
DATA: i_stats TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF t_stats,
r_stats TYPE t_stats,
r_statsora TYPE t_statsora,
l_kount TYPE i.
DATA: secs(2) TYPE n,
rndnum TYPE i,
iscreated TYPE i.
CONSTANTS: allmychoices(44) TYPE c VALUE
'ProgFuncBAdIFormSmrtObjtTcodWbObTblsHelpWhlp'.
DATA: schema(30) TYPE c,
idxnum(1) TYPE n,
windexname(30) TYPE c,
posnum TYPE dd03l-position,
wfieldname(30) TYPE c,
fldname TYPE string.
FIELD-SYMBOLS: LIKE r_stats-index2.
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
* SELECTION-SCREEN DESIGN
*
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
SELECTION-SCREEN: BEGIN OF BLOCK b1sels WITH FRAME TITLE text-001.
SELECT-OPTIONS: stabname FOR dd02l-tabname. "Abap
table
SELECTION-SCREEN: END OF BLOCK b1sels.
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
* INITIALIZATION EVENT
*
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
INITIALIZATION.
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
* AT SELECTION-SCREEN VALUE-REQUEST EVENT
*
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
* AT SELECTION-SCREEN EVENT
*
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
* START-OF-SELECTION EVENT
*
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
START-OF-SELECTION.
PERFORM f_validation.
PERFORM f_retrieve_data.
PERFORM f_process_data.
PERFORM f_display_data.
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Form F_VALIDATION
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
FORM f_validation.
ENDFORM. " F_VALIDATION
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Form F_RETRIEVE_DATA
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
FORM f_retrieve_data .
SELECT dd02v~tabname "ABAP TableBName
dd02v~tabclass
dd02t~ddtext
INTO CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF TABLE i_stats
FROM dd02v INNER JOIN dd02t
ON dd02v~tabname = dd02t~tabname
AND dd02v~ddlanguage = dd02t~ddlanguage
AND dd02t~ddlanguage = sy-langu
WHERE dd02t~tabname IN stabname.
SELECT sqltab AS tabname "ABAP TableBName
sqlclass AS tabclass
ddtext
APPENDING CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF TABLE i_stats
FROM dd06v
WHERE ddlanguage = sy-langu
AND sqltab IN stabname.
ENDFORM. " F_RETRIEVE_DATA
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Form F_PROCESS_DATA
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
FORM f_process_data .
LOOP AT i_stats INTO r_stats.
MOVE 0 TO l_kount.
EXEC SQL.
open c1 for
select a.num_rows,
a.avg_row_len,
TO_CHAR(a.last_analyzed,'YYYYMMDD') As last_analyzed
from USER_tables a
where a.table_name = :r_stats-tabname
ENDEXEC.
DO.
EXEC SQL.
fetch next c1 INTO :R_STATSORA
ENDEXEC.
IF sy-subrc <> 0.
EXIT.
ENDIF.
MOVE-CORRESPONDING r_statsora TO r_stats.
EXIT.
ENDDO.
EXEC SQL.
close c1
ENDEXEC.
r_stats-index0 = 'PK('.
SELECT fieldname
position
INTO (wfieldname, posnum)
FROM dd03l
WHERE tabname = r_stats-tabname
AND keyflag = 'X'
ORDER BY position.
IF r_stats-index0 = 'PK('.
CONCATENATE r_stats-index0 wfieldname INTO
r_stats-index0.
ELSE.
CONCATENATE r_stats-index0 ',' wfieldname INTO
r_stats-index0.
ENDIF.
ENDSELECT.
CONCATENATE r_stats-index0 ')' INTO r_stats-index0.
idxnum = 0.
SELECT indexname
fieldname
position
INTO (windexname, wfieldname, posnum)
FROM dd17s
WHERE sqltab = r_stats-tabname
ORDER BY indexname position.
IF posnum = 1.
IF idxnum <> 0.
CONCATENATE ')' INTO .
ENDIF.
ADD 1 TO idxnum.
IF idxnum > 7.
CONCATENATE r_stats-index6 ' more!!!' INTO
r_stats-index6 .
EXIT.
ENDIF.
CONCATENATE 'R_STATS-INDEX' idxnum INTO fldname.
ASSIGN (fldname) TO .
CONCATENATE windexname '(' wfieldname INTO .
ELSE.
CONCATENATE ',' wfieldname INTO .
ENDIF.
ENDSELECT.
IF idxnum <> 0.
CONCATENATE ')' INTO
ENDIF.
MODIFY i_stats FROM r_stats.
ENDLOOP.
ENDFORM. " F_PROCESS_DATA
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Form F_DISPLAY_DATA
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
FORM f_display_data.
* Macro definition
DEFINE m_fieldcat.
ls_fieldcat-fieldname = &1.
ls_fieldcat-tabname = &2.
ls_fieldcat-ref_fieldname = &3.
ls_fieldcat-ref_tabname = &4.
ls_fieldcat-seltext_l = &7.
ls_fieldcat-seltext_m = &7.
ls_fieldcat-seltext_s = &7.
ls_fieldcat-reptext_ddic = &7.
ls_fieldcat-hotspot = &5.
ls_fieldcat-fix_column = &6.
append ls_fieldcat to lt_fieldcat.
END-OF-DEFINITION.
DEFINE m_sort.
ls_sort-tabname = &1.
ls_sort-fieldname = &2.
ls_sort-up = 'X'.
append ls_sort to lt_sort.
END-OF-DEFINITION.
DATA:
ls_fieldcat TYPE slis_fieldcat_alv,
lt_fieldcat TYPE slis_t_fieldcat_alv," Field catalog
ls_sort TYPE slis_sortinfo_alv,
lt_sort TYPE slis_t_sortinfo_alv," Sort table
ls_keyinfo TYPE slis_keyinfo_alv,
ls_layout TYPE slis_layout_alv.
ls_layout-box_tabname = 'I_STATS'.
ls_layout-min_linesize = 240.
ls_layout-window_titlebar = 'Index Info & Oracle Statistics'..
ls_layout-colwidth_optimize = 'X'.
m_fieldcat 'TABNAME' 'I_STATS' 'TABNAME' 'DD02T' '
' 'X' 'Table Name'.
m_fieldcat 'TABCLASS' 'I_STATS' 'TABCLASS' 'DD02V' '
' ' ' 'Class'.
m_fieldcat 'NUM_ROWS' 'I_STATS' 'STYLE' 'ABDEMONODE' '
' ' ' 'Num Rows'.
m_fieldcat 'AVG_ROW_LEN' 'I_STATS' 'STYLE' 'ABDEMONODE' '
' ' ' 'Avg.RowLen'.
m_fieldcat 'LAST_ANALYZED' 'I_STATS' 'BUDAT' 'EKBE' '
' ' ' 'LastAnalyzed'.
m_fieldcat 'DDTEXT' 'I_STATS' 'DDTEXT' 'DD02T' '
' ' ' 'Description'.
m_fieldcat 'INDEX0' 'I_STATS' 'MATKX' 'MAKT' '
' ' ' 'PrmKey'.
m_fieldcat 'INDEX1' 'I_STATS' 'MATKX' 'MAKT' '
' ' ' 'Index1'.
m_fieldcat 'INDEX2' 'I_STATS' 'MATKX' 'MAKT' '
' ' ' 'Index2'.
m_fieldcat 'INDEX3' 'I_STATS' 'MATKX' 'MAKT' '
' ' ' 'Index3'.
m_fieldcat 'INDEX4' 'I_STATS' 'MATKX' 'MAKT' '
' ' ' 'Index4'.
m_fieldcat 'INDEX5' 'I_STATS' 'MATKX' 'MAKT' '
' ' ' 'Index5'.
m_fieldcat 'INDEX6' 'I_STATS' 'MATKX' 'MAKT' '
' ' ' 'Index6'.
CALL FUNCTION 'REUSE_ALV_LIST_DISPLAY'
EXPORTING
is_layout = ls_layout
it_fieldcat = lt_fieldcat
TABLES
t_outtab = i_stats.
IF sy-subrc <> 0.
MESSAGE ID sy-msgid TYPE sy-msgty NUMBER sy-msgno
WITH sy-msgv1 sy-msgv2 sy-msgv3 sy-msgv4.
ENDIF.
ENDFORM. " F_DISPLAY_DATA
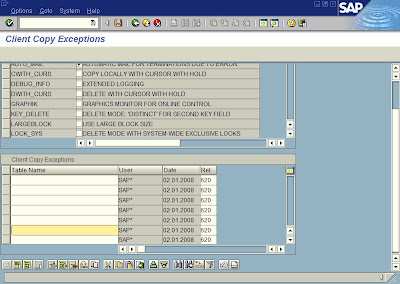
How to exclude a table in client copy in SAP
Goto transaction SA38 , enter the report name and execute. You will see the output screen as
Bandwidth requirement of ISP to connect to SAP server through VPN
We are in the process of implementing SAP for our overseas sales offices. However, the Server will be situated at our country. We want our overseas sales office to connect to our SAP Server through VPN. What should be the optimum internet bandwidth that they should use at their place to connect to our SAP server? Does SAP recommend any standard bandwidth for this process?
From our experience, there is no general rule that one can follow, as several factors will affect the connectivity
1. No of hops between your ISP and that of the remote site, the more hops the poorer the performance, even having large bandwidth may not improve the performance by much if there are numerous hops in between.
2. Is the Internet connectivity solely used for your VPN or other purposes such as web surfing, email etc, other traffic can consume large amount of traffic thus causing your SAP performance to be poorer
3. ISP's bandwidth to the public internet - If the ISP is heavily over subscribed, and has limited bandwidth connecting to the international network, you will find that you will not be able to get the international throughput you subscribed for as such, performance may be poor even you have paid for a line with a large bandwidth
4. No of users at your remote office using the VPN - In general the lines we use are 64kbps for sites with approx 3-5 users, we are also using ADSL lines with 512kbps connectivity and they enjoy close to local Lan performance for SAP.
See from which network IP address and host name a user has logged on
To see the network IP address from which a user has logged on,
perform the following steps:
Call transaction OS01,
click "Presentation Server" button, "Change View" button.
If you are using Citrix, you will not be able to view the user individual IP address as it will be the same Citrix IP address.
To check the speed and quality of the user's network connection,
select the desired presentation server and click "10 X Ping" button.No System name and transaction code in SM04
If you have more than one application server, use AL08 instead of SM04.
or
It is because they are at the logon screen which has established a connection.
You will notice that the transaction code shown when there is no user name is SESSION_MANAGER.
This shows you which workstations out there have the login screen up but have not yet entered a user name and password.
The transaction column shows the Last executed transaction code.
Sometimes your users will have multiple sessions open. If they do, to the system, it is the same as multiple logins as it relates to the resources used etc.
So the user name will show up more than once in AL08.
Under the application server they are logged into, each instance of that user name on that application server represents a session open.
For instance if you run AL08, you will have your name show up at least twice on the application server you are logged into.
One will show AL08 and the other will not have a transaction next to it.
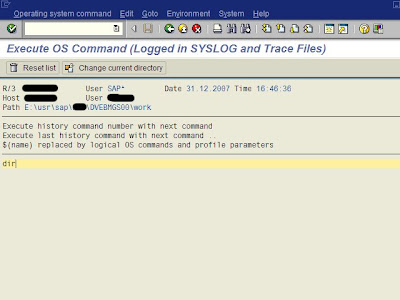
Then you will notice your user name showing up on all other application servers with no transaction. This is because you are using AL08.How to execute and External OS command in SAP
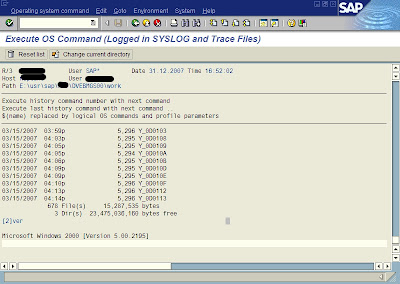
Then enter the command you want to execute. In this example i am using command DIR
Then press enter key , you will see the output as
Thursday, July 10, 2008
Basis - Message Class - System Message
Configure System Messages
For example, when a user blocks himself out and receives a message :
"User blocked. Contact system administrator"
You can open a repair and change the message in Message class 00.
This can be done in transaction SE91 - Message Maintenance.
Messages allow you to communicate with the users from your programs.
They are mainly used when the user has made an invalid entry on a screen.
To send messages from a program, you must link it to a message class.
Each message class has an ID, and usually contains a whole set of message. Each message has a single line of text, and may contain placeholders for variables (e.g. & & & - three variables).
All messages are stored in table T100.
Once you have created a message, you can use it in the MESSAGE statement in a program.SAP Notes Assistant
SAP notes assistant is a tool with which you implement or import a sap note. Sap notes are released in SAP systems with a specific support package level. Some times they are also released to include added functionalities in the system. SAP notes include a description of the symptoms, the cause of the error, and the SAP Release and Support Package level in which the error occurs. SAP notes may also contain attached files which has ABAP programs. They can be imported into the system using TMS. Depending on the type of error, an SAP Note may also include descriptions of how to correct the source code which are called correction instructions.
Before implementing read the Pre-requisites of SAP notes carefully
The steps to be followed are
- Login to the SAP service market place and download the SAP notes containing correction instructions to the front-end.
- Upload the notes from the frontend to the system using SAP notes assistant (Transaction SNOTE)
- If you know the sap notes number you can download it by using assistant. Click on the button
 and enter the SAP notes number.
and enter the SAP notes number. - Then the sap notes is implemented if its status is new ( click on button
 )
)
The uses of using note assistant are
- It keeps a track of the processing status of all the SAP notes in the system
- The notes can be de-implemented
- It check consistency of SAP notes with the release of SAP system
- It maintains the processing status of SAP notes
The notes assistant is an add-on. One has to import it from SAP service market place and install it in the system by using SAINT.
Note: When implemented SAP notes changes the ABAP code only. The ABAP dictionary objects are not changed. This has to be done manually before implementing SAP notes so that the pre-requisites are met.
Suspend/UnSuspend Released ABAP Jobs
BTCTRNS1 - Suspend all Released Jobs
Released Jobs will have the status Released/Susp. in transaction SM37.
BTCTRNS2 - Reverse Suspend for all Released Jobs
What Is The Job Name EU_REORG Meant?
OSS is your friend - see note 18023:
1. When starting Transaction SE80 for the first time, the three EU jobs are scheduled automatically: EU_INIT (single start), EU_REORG (periodically each night), and EU_PUT (periodically each night).
Alternatively,those three EU jobs can also be scheduled by manually executing program SAPRSEUJ.
Shortdescription of the individual jobs:
EU_INIT:
EU_INIT serves for completely rebuilding the indices and therefore has a correspondingly long runtime. It starts program SAPRSEUI. All customer-defined programs (selection according to the name ranges) are analyzed, and an index is created that is used in the DW for the where-used lists for function modules, error messages, reports, etc.
Starting in Release 2.1, this index is automatically updated online. The job can be repeated at any time. After a termination, the job is automatically scheduled for the next day; it then starts at the point oftermination. (EU_INIT can therefore be terminated deliberately, if it disturbsother activities in the system.)
EU_REORG:
As mentioned above, the indices are automatically updated online by the tools. To keep the effort for updating these indices as low as possible, only the changes are logged, which means a reorganization of the complete index for each program is required from time to time. To avoid having this reorganization interfere with online work, job EU_REORG runs every night and performs this task. If job EU_REORG did not run one night, this simply means that thereorganization takes place more often online.
SAP Courses & Certifications for SAP Basis Admins
My goal is the SAP Basis Certification!
Of course experience is valued higher than (theoretical) knowledge, but especially in the SAP world the certification is your must-have entrance ticket to verify your skills.
I know what you're thinking about... Braindumps.
From my previous exam as Microsoft Certified Professional I know the value of brain dumps, but in the matter of an SAP exam you can forget cheating:
- even in the deepest and darkest corners of top insider discussion forums, there are no secret guides for SAP Certifications available
- the level of relevant certification knowledge is so broad, that without a very deep understanding of the theme you'll just waste money for the exam
- and finally you can't cheat at work - every SAP Basis job requires comprehensive knowledge, without you'll be fired after your first day. Promised!
Have a look at this certifcation path to become a SAP Certified Technology Consultant (SAP Basis Admin):

TADM10 (description here) is mandatory not only for the Basis Administrator, but also i.e. for the education path to XI/PI consultants.
Together with TADM12 (description here), both courses covers following separate available courses:
- ADM100: SAP Web AS Administration I
- ADM102: SAP Web AS Administration II
- ADM200: SAP Web AS Java Administration
- ADM110: Installation SAP ECC 6.0
- ADM325: Software Logistics
- ADM315: Workload Analysis
After TADM10&12, you have to decide which DBMS you'll work with.
I will take the path to Oracle = TADM51 (description here)
Again, TADM51 covers some separate available courses:
- ADM505: Database Administration Oracle I
- ADM506: Database Administration Oracle II
Interview Questions for SAP Basis
Interview Questions for SAP Basis
What is private mode? When does user switch to user mode?
Private mode is a mode where the heap data is getting exclusively allocated by the user and is no more shared across the system. This happens when your extended memory is exhausted.
What is osp$ mean? What if user is given with this authorisation?
OPS$ is the mechanism the
Why do you use DDIC user not SAP* for Support Packs and SPam?
Do _NOT_ use neither DDIC nor SAP* for applying support packages. Copy DDIC to a separate user and use that user to apply them.
Can you kill a Job?
Yes - SM37 - select - kill
If you have a long running Job, how do you analyse?
Use transaction SE30.
How to uncar car/sar files in a single shot?
on Unix:
$ for i in *.SAR; do SAPCAR -xvf $i; done
When we should use Transactional RFC ?
A "transactional RFC" means, that either both parties agree that the data was correctly transfered - or not. There is no "half data transfer".
What is the use of Trusted system. I know that there is no need of UID and PWD to communicate with partner system. In what situation it is good to go for Trusted system ?
E. g. if you have an R/3 system and a BW system and don't want to maintain passwords. Same goes for CRM and a lot of other systems/applications.
Let me know if my understanding below is correct:
1) By default the RFC destination is synchronous
2) Asynchronous RFC is used incase if the system initiated the RFC call no need to wait for the response before it proceeds to something else.
Yes - that's right.
But keep in mind, that it's not only a technical issue whether to switch to asynchronous. The application must also be able to handle that correctly.
Which table contains the details related to Q defined in SPAM? Is there a way to revert back the Q defined? If yes, How?
There is a "delete" button when you define the queue. If you already started the import it's no more possible since the system will become inconsistent.
What is a developer key? and how to generate a developer key?
The developer key is a combination of you installation number, your license key (that you get from http://service.sap.com/licensekey) and the user name. You need this for each person that will make changes (Dictionary or programs) in the system.
What is XI3.0 ? EXPLAIN XI = Exchange Infrastructure - Part of Netweaver 2004.
SAP Exchange Infrastructure (SAP XI) is SAP's enterprise application integration (EAI) software, a component of the NetWeaver product group used to facilitate the exchange of information among a company's internal software and systems and those of external parties. Like other NetWeaver components, SAP XI is compatible with software products of other
companies.
SAP calls XI an integration broker because it mediates between entities with varying requirements in terms of connectivity, format, and protocols. According to SAP, XI reduces integration costs by providing a common repository for interfaces. The central component of SAP XI is the SAP Integration Server, which facilitates interaction between diverse operating systems and applications across internal and external networked computer systems.
How to see when were the optimizer stats last time run? We are using win2k, oracle 9, sapr346c.
Assumed DB=Oracle
Select any table lets take MARA here but you should do the same for MSEG and few others to see whether the dates match or not.Run the following command on the command prompt:-
select last_analyzed from dba_tables where table_name like '%MARA%';
This gives you a straight answer .Else you can always fish around in DB14 for seeing when the optimzer stats were updated.*--
SAP Administration Questions Answers
SAP Administration Questions Answers
What is the use of profile paramater ztta/roll_area?
The value specifies the size of the roll area in bytes. The roll area is one of several memory areas, which satisfies the user requests of user programs. For technical reasons, however, the first 250 KB or so of a user context are always stored in the roll area, further data
- up to the roll area limit ztta/roll_first,
- in the extended memory, up to the limit ztta/roll_extension or if extended memory is exhausted, then
- again in the roll area, until the roll area is full, then
- in the local process area, up to the limit abap/heap_area_dia or abap/heap_area_total or until the address space or the
swap space is exhausted.
Followed by termination with errors like STORAGE_PARAMETERS_WRONG_SET an error code, that points to memory bottleneck Minimum data transfer with context change; however, the increase helps to avoid problems (address space, swap space, operating system paging). *-- Anupam Sharma
What is R/3? and what is basis version?
SAP Basis:
- Provides the runtime environment for all SAP applications
- Optimally embeds the application in the system environment
- Defines a stable architecture framework for system enhancements
- Contains the tools for administering the entire system
- Allows the distribution of resources and system components
- Provides interfaces for decentralized system parts and external products.
An R/3 instance is a group of R/3 services that are started and stopped as a unit (by an R/3 dispatcher) and have a common instance profile. The name of an R/3 instance is composed of letters standing for the relevant services, and an instance number which is unique for each computer. The services may be D, V, E, B, M, G, or S, which respectively stand for dialogue, update, enqueue, background, message, gateway, and spool services.
Tips by : Suresh Babu
I would like to know the version or name of SAP that is implemented in real time?
This is a very generic question and really depends on what you are implementing (modules).
The history of the "R/3" is
3.0D Basis 300
3.0E Basis 300
3.0F Basis 300
3.1H Basis 310
3.1I Basis 310
4.0B Basis 400
4.5B Basis 450
4.6C Basis 460
4.71 Basis 6.20
4.72 Basis 6.20
5.00 Basis 6.40 (ECC 5.0 - Enterprise Core components)
6.00 Basis 7.00 (ECC 6.0) - actually in RampUp
All of those have increased business functionality and interfaces to other systems (CRM, BW etc.)
What is mysap?
It's a term for all the systems that in a contract (e. g. a MySAP business suite consist of ERP2005, CRM2005, SRM2005).
What is the systems configuration required to implement SAP.. i.e for production,development and QAS servers the hard disk space, RAM, Processor
This also depends on what your are implementing, how many users will work on the system, how many records in what area are created etc.
We need a BIG database system and an even bigger application server for ~ 900 users and 12 languages.
What is ASAP?
It's an old term for an implementation strategy. Blueprint -> prototype -> goLive (if you want to say it in one sentence).
How should I set priority for Printing say like user, teamlead, project manager?
There's nothing like "priority" settings for spool processes. Just define more (profile parameter rdisp/wp_no_spool) processes so people don't need to wait.
Using Tc SGEN I have generated 74% job and later I have terminated the job. I wish to start generating from where it stopped I have refreshed but to no chance nothing was done. How should I further proceed so as to complete the remaining job..
Start SGEN again and select the same you have selected before. It will popup and ask if you want to start from scratch or generate the just the remaining.
SAP Basis FAQ
SAP Basis FAQ
Automatic CTS
Even though SAP does not recommend automatic imports, it is the most practical way of moving transports from a development system to a QA environment or to a special development system (although I wouldn't recommend auto imports to a production system for obvious reasons).There are various methods for doing this. The most effective and simple method is using an OS script (shell/perl etc.) scheduled using cron for user sidadm. There are a couple of steps you need to take before setting up automatic imports.
- Your entire project team should agree upon the overall strategy, frequency of imports etc.
- Resolve any issues with transport approvals (many shops don't care about traffic between DEV and QA)
- Who is responsible for watching for errors and corrective actions (an email to the developer works in this case)
Configuring outbound SAP to Internet mail Gateway (R/3 4.0 and above)
Step 1 (UNIX SETUP)Logon to your
Change directory to /sapmnt/SID/global (or any directory globally available across all application servers)
Create the following entries in file SAP_EMAIL_GATEWAY.sh and save the file
#!/bin/shExecute the command: mlosmadm SAP_EMAIL_GATEWAY.cfg (enter the following information)
GWCONFIG=/sapmnt/SID/global/SAP_EMAIL_GATEWAY.cfg
export GWCONFIG
/sapmnt/SID/exe/mlunxsnd $*
System name : SIDStep 2 (SAP SETUP)
Client : 200
Username : MAILADM
Password : initpass
Language : E
Loadbalancing : Y
Message Server :
Group name : LOGON GROUP1
Using SAPROUTER : N
Trace Level (inBoound) : 0
Sendmail Command :
Codepage :
Trace Level (Outbound) : 0
Update file : Y
Logon to SAPSYSTEM (SID) via SAPGUI
Transaction SU01, create user MAILADM and password initpass, usertype CPIC
Transaction SM59, Click Create
RFC Destination : SAP 4.5 INTERNET MAIL GATEWAYTransaction SCOT, click Edit--> CREATE NODES
Connection Type : T
Description : INTERNET EMAIL GATEWAY
Hit RETURN
Click EXPLICIT HOST
Enter /sapmnt/P21/global/ SAP_EMAIL_GATEWAY.sh
Save your entries
Node : EMAIL
Description : SAP CONNECT NODE FOR EMAIL (continue)
RFC DESTINATION: (choose SAP 4.5 INTERNET MAIL GATEWAY from the pull down menu)
Choose radio button Internet
Address area : *DOMAIN (your intranet domain)
Ccontinue
Format : DOC, DAT, R3F, TXT, RAW,PPT,XLS (continue)
Continue
Set further address types : N
Minimum waiting : 5 minutes
Check both Node is in use', Node can resolve path references
Continue
Choose Goto--> Schedule Background Job
Enter name for the job & save
Configuring outbound SAP to Internet mail Gateway (Upto R/3 3.1I)
SAP can be configured to send and receive emails from different sources. This section explains how to integrate SAPOffice with an external email system. This is in no way supplementing the online documentation available on the online documentation CD supplied by SAP but simplyfies the process to the bare Internet email must be configured and running prior to this. Email from SAP is forwarded to the users external email client such as Eudora, Outlook etc.You can configure inbound and outbound forwarding. Outbound flow forwards a SAP message (eg:update termination) via UNIX sendmail to the intended recepient. Inbound accepts a message from sendmail and places it in the users SAPOffice inbox. Many SAP shops prefer to configure outbound only.
Configuring outbound forwarding
SAP configuration
- Create your RFC destination for outbound email using transaction SM59
RFC Destination : SAP_INTERNET_GATEWAY
Connection Type : T
Description : SAP internet mail gateway
Click on 'Explicit Host' if you want on demand gateway dameon invocation.
Program : /sapmnt/SID/exe/mlunxsnd
Target Host : Enter hostname that runs your central instance.
Click 'Test Connection' and you should see a successfull message. - Choose menu Tools-->Administration-->Management-->Process Technology-->Office-->Office Settings
- Click Internet Gateway
Gateway Destination : SAP_INTERNET_GATEWAY
Path for configuration file : /sapmnt/SID/exe/sap_mailSID.cfg
Return Address : .com - Click Internet Settings and fill in the following fields
- Save the settings
- Click Back
- Choose menu Office-->Addresses-->Communication Types
- Type in INT over the Comm. type and Internet Mail over description.
- . Check Maintain and Send checkboxes and Save your entries.
- . cd /sapmnt/SID/exe
-
UNIX configuration
.mlosadm sap_mailSID.cfg
Client 000
Username : MAILADM
Password : MAILADM
Language : E
System name : SID
System number :
Hostname :
Gateway hostname:
Gateway server sapgw
Sendmail Command :
Update file : YTesting
- Logon to SAP
- Execute transaction SO01
- Write a message and send it to
If you don't see the mail in your internet mailbox, go back and review steps 1-12
FTP from ABAP
There are 2 ways of executing FTP from an ABAP (online or batch mode),| Initiated from the operating system. A script is available in the utility repository that explains how to do this very easily. | |
| Initiated from the ABAP itself An example is given below. |
- Create a logical OS command 'zftp' using transaction SM69. Make sure that you enable 'comand line parameter allowed' checkbox
- Create a shell script called 'zftp' with the following lines
RMTHOST=`echo $2 | tr '[A-Z]' '[a-z]'`
ftp -v $RMTHOST <<> /out/zftp.$$ 2>&1
lcd /out
put $1
bye
EOF - Use the SXPG_COMMAND_EXECUTE function module to call this script (zftp) with the filename you want to transfer as the parameter. Eg:
call function 'SXPG_COMMAND_EXECUTE'
exporting
commandname =
tables
exec_protocol =
exceptions
no_permission = 1
command_not_found = 2
parameters_too_long = 3
... Enable web based online documentaion (R/3 4.0 or above)
- Install Netscape webserver or use an existing web server (requires administrators privelege)
- Create a directory called SAPDOCS4 under your web server document root.
- Mount the CDROM containing online documentation on your PC or your UNIX server.
- Recursively copy all files under /cdrom/docs/ to the SAPDOC4 directory under the web server root.
- Create the following entries in your /usr/sap/SID/SYS/profile/DEFAULT.PFL
eu/iwb/installed_languages = EN
eu/iwb/help_type=2
eu/iwb/server_win32=webserver.domain.com
eu/iwb/path_win32=saphelp/helpdata
- Restart your SAP system
How to access an external database from ABAP via DBLINK (ORACLE)
- Using transaction SE11, create a table (ZTABLE) with the same fields as the table in the external database, make sure that the type and lengths of the fields are identical.
- Using transaction SE11, create a view (ZTABLE_VIEW, projection view) using BASIS table ZTABLE
- Using SVRMGRL>
create dblink REMOTE_DB as connect to remote_user identified by password; (database link created)
drop table ZTABLE; (table dropped)
create synonym ZTABLE for ZTABLE@REMOTE_DB; (synonym created)
- Using transaction SE16 , type in ZTABLE_VIEW and hit RETURN
- Enter value in key fields and hit execute. (displays rows from the remote table)
Tips and Tricks
- To see the complete text of an error/warning message on the SAPGUI status bar, right click on the message and drag left.
- To prevent your spool requests getting deleted from the BASIS cleanup jobs, you need to uncheck the Delete after print checkbox in the print control screen, execute transaction SP01, find your spool#, click on Attributes and change the Delete After date
- Short cuts using the OK-code box.
%scSearch in page%pcDownload do local filep+Page upp-Page downp++Top of pagep--End of page
- Use transaction AL11 to browse the application servers directory structure.
Archives
-
▼
2008
(137)
-
▼
July
(56)
- Useful SAP System Administration Transactions
- Changing the Title of SAP Transaction
- Search for SAP Basis Transaciton codes
- How to list all transactions executable for a role.
- List of Tcodes executable for a User in SAP
- How to view recently accessed transactions by user...
- How to find sap transaction codes IN SAP
- Sap Basis Transaction Codes 343
- Changing the Title of SAP Transaction
- Basis Tables Reorganization of Single Object
- How to Increase the Tablespace free space?
- How to activate the IMG Change Log?
- Basis - Edit, create, delete or adjust your databa...
- Finding any of the SAP tables that have been changed
- Transport Tables between Clients
- Copying table entries from client 000
- SAP Transaction Table
- SAP Tablespace sizes in large databases
- SAP SQL Tuning Aid with Oracle RDBMS Statistics
- How to exclude a table in client copy in SAP
- Bandwidth requirement of ISP to connect to SAP ser...
- See from which network IP address and host name a ...
- No System name and transaction code in SM04
- How to execute and External OS command in SAP
- Basis - Message Class - System Message
- SAP Notes Assistant
- Suspend/UnSuspend Released ABAP Jobs
- What Is The Job Name EU_REORG Meant?
- SAP Courses & Certifications for SAP Basis Admins
- Interview Questions for SAP Basis
- SAP Administration Questions Answers
- SAP Basis FAQ
- Basis Administration Questions Answers
- Administration SAP Administrator Daily Activities
- Tcodes used for Daily System Monitoring
- Monitor and Administrate 4 SAP Systems
- Brief Description About SAP Basis Implementation
- How to Check Missing Authorisation for User
- SAP Profile Generator tables
- Frequently Asked Questions on Authorization
- Query About Tcode PFCG
- How To Compare The Roles
- Creating New User With Authorizations
- How To Provide All Rights To The User
- Archiving and Reorganization are totally different...
- Archiving the Material Master
- Deletion of Vendor Consignment Records
- Reasons For Archiving Financial Accounting Data
- Archiving and Reorganization are totally different...
- Archiving the Material Master
- Deletion of Vendor Consignment Records
- Reasons For Archiving Financial Accounting Data
- SAP Administrator Daily Activities
- Tcodes used for Daily System Monitoring
- Monitor and Administrate 4 SAP Systems
- Brief Description About SAP Basis Implementation
-
▼
July
(56)





